前言
在 C 语言中有指针,指针通过地址来寻找元素。在 python 中,变量本质上存储的是地址,所以在 python 中可以通过把节点作为变量传递给另一个变量,就完成了类似于 C 语言中指针域的功能。
单链表结构
单链表是一种常见的数据结构,由一个个节点串联而成,每个节点一般有两个变量,一个是数据域——用于保存数据;另一个是指针域——指向下一个节点,可通过指针域来寻找位于该节点之后的节点。
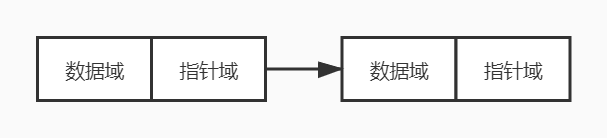
单链表定义
根据单链表的结构,可以抽象出单链表节点的定义,包含数据域和指针域,如下:
class ListNode:
"""节点"""
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x # 数据域
self.next = None # 指针域
单链表包含头节点 head 和记录链表长度的 length,如下:
class SingleLinkList:
"""单链表"""
# 初始化
def __init__(self):
self.head = None # 头节点
self.length = 0 # 链表长度
这样就完成了单链表的定义。
单链表基本操作
判断链表是否为空
class SingleLinkList:
"""单链表"""
# 判断单链表是否为空
def is_empty(self):
return not self.head
头插法
class SingleLinkList:
"""单链表"""
# 头插法
def add(self, node):
node.next = self.head
self.head = node
self.length += 1
尾插法
class SingleLinkList:
"""单链表"""
# 尾插法
def append(self, node):
cur = self.head
if self.is_empty(): # 如果当前链表为空
self.head = node # 将头节点指向插入节点
else:
while cur.next: # 遍历找到尾节点
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node # 让尾节点的 next 指针域指向新节点
self.length += 1
指定位置插入元素
class SingleLinkList:
"""单链表"""
# 指定位置插入,index 为索引值,从 0 开始计数
def insert(self, node, index):
cur = self.head
if index > self.length or index < 0: # 下标越界
print("插入位置不正确")
return
if index == 0: # 如果在头部插入,等同于头插法
self.add(node)
else: # 找到插入位置的前一个节点
for i in range(0, index - 1):
cur = cur.next
node.next = cur.next # 在该节点之后插入新节点
cur.next = node
self.length += 1
遍历
class SingleLinkList:
"""单链表"""
# 遍历单链表
def travel(self):
cur = self.head
if self.is_empty(): # 空链表
print("单链表为空")
return
num = 1
print("单链表长度为:", self.length)
while cur:
print("第{}个元素为:{}".format(num, cur.val))
num += 1
cur = cur.next
删除节点
class SingleLinkList:
"""单链表"""
# 删除节点
def remove(self, item) -> bool:
if self.is_empty():
print("单链表为空")
return False
cur = self.head # 保存遍历节点
pre = self.head # 保存遍历节点的前一个节点
while cur:
if cur.val == item: # 找到相等数据域的节点
if cur == self.head: # 如果恰好是头节点,删除头节点
self.head = cur.next
else: # 非头节点,删除当前节点
pre.next = cur.next
self.length -= 1
return True
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return False
查找节点
class SingleLinkList:
"""单链表"""
# 查找节点
def search(self, item) -> bool:
cur = self.head
while cur:
if cur.val == item:
return True
cur = cur.next
return False



