一。 前言
本文主要介绍 Gin 中的路由的基本使用,包括基本路由、路由分组、路由传参和参数校验。
二。 路由
基本路由
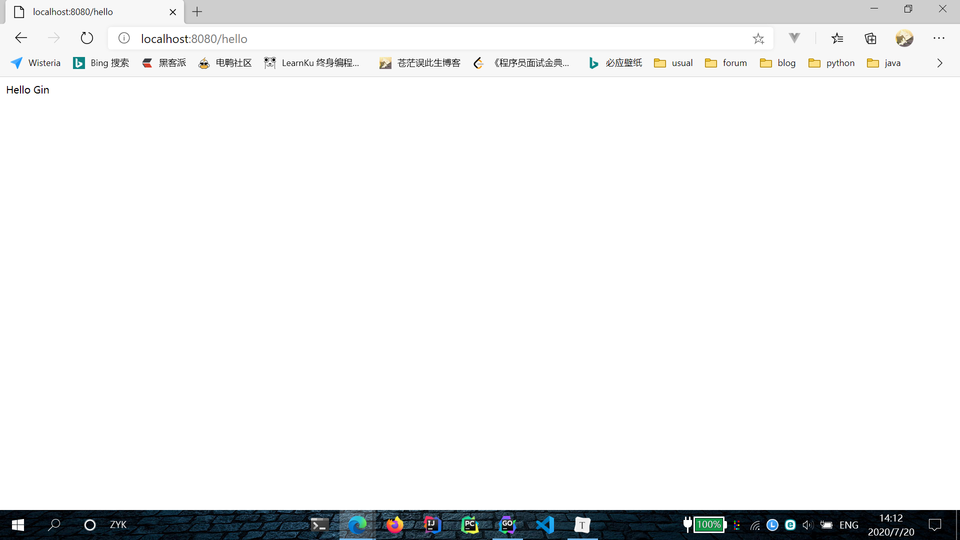
通过 gin.Default() 获取默认中间件 router,调用 GET 函数表示 GET 类型的请求;"/hello" 表示请求的 URL;在回调函数 func 中利用 context.String 返回值为 Hello Gin 的字符串。
func 回调函数中的 gin.Context 是 Gin 框架重要组成部分,可以用来处理请求数据和中间件。
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin" // 导入 gin 依赖
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// 获取默认中间件
router := gin.Default()
// GET 请求
router.GET("/hello", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.String(http.StatusOK, "Hello Gin")
})
// POST 请求
router.POST("/hello", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.String(http.StatusOK, "POST Method")
})
// 指定端口,运行 Gin
err := router.Run(":8080")
// 异常处理
if err != nil {
log.Panicln("服务器启动失败:", err.Error())
}
}
运行项目,在浏览器中访问 localhost:8080/hello ,页面将会显示 Hello Gin。
路由分组
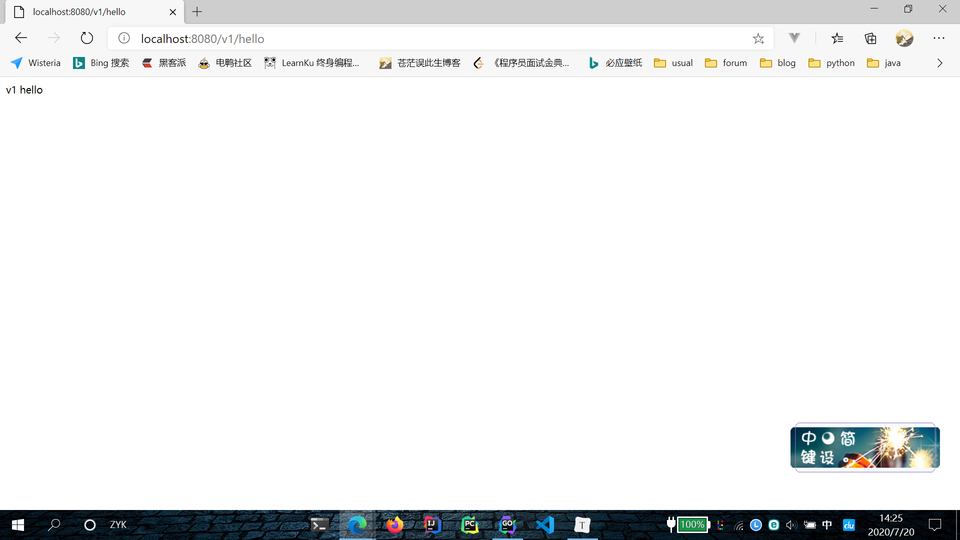
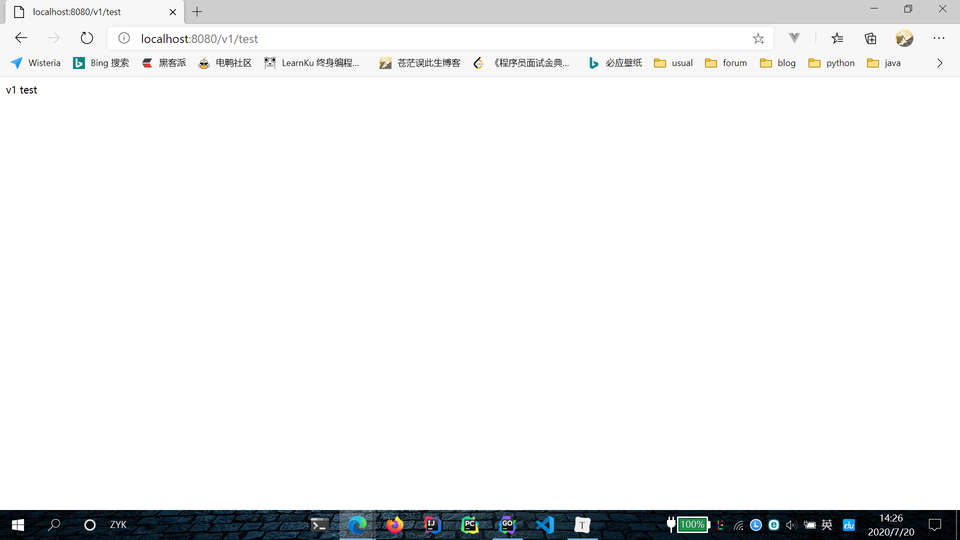
通过调用 Group 函数,来实现路由分组。Group 函数中的 "v1" 表示 URL 根路径,嵌套在其中的两个函数表示子路由,两个路由参数拼接在一起,实现了 "/v1/hello" 和 "/v1/test" 两个路由。
// 路由分组
v1 := router.Group("/v1")
{
// /v1/hello
v1.GET("/hello", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.String(http.StatusOK, "v1 hello")
})
// /v1/test
v1.GET("/test", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.String(http.StatusOK, "v1 test")
})
}
运行项目,在浏览器中依次访问 http://locahost:8080/v1/hello 和 http://locahost:8080/v1/test,观察页面内容。
路由传参
-
通过 Query 传参
Query 传参是指形如
http://localhost:8080/query?id=1&name=zhangsan的传参形式。http://localhost:8080/query?id=1&name=zhangsan传递了两个参数id和name,id的值为1,name的值为zhangsan;第一个参数前面必须使用?,=表示该参数的值,第二个参数起必须使用&进行拼接;所以如果要传递第三个参数,继续用&拼接即可,例如http://localhost:8080/query?id=1&name=zhangsan&age=18。在 Gin 中可以通过
context.Query("id")函数来接收参数,"id"表示参数名称,如果该参数不存在,将返回空字符串。// 通过 Query 传参 router.GET("/query", func(context *gin.Context) { id := context.Query("id") name := context.Query("name") log.Println("id: ", id) log.Println("name: ", name) })运行项目,在浏览器中访问
http://localhost:8080/query?id=1&name=zhangsan,观察Goland控制台信息。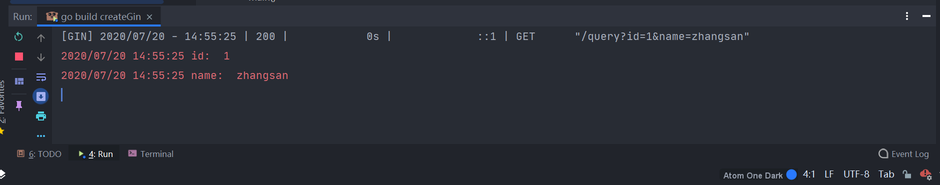
-
通过 Param 传参
Param 传参是指形如
http://localhost:8080/param/1的传参形式,/后面拼接参数的值。在 Gin 中可以通过在路由中指定
":参数名称",同时通过context.Param("参数名称")来获取参数的值。// 通过 Param 传参 router.GET("/param/:id", func(context *gin.Context) { id := context.Param("id") log.Println("id: ", id) })运行项目,在浏览器中访问
http://localhost:8080/param/1,观察 Goland 控制台信息。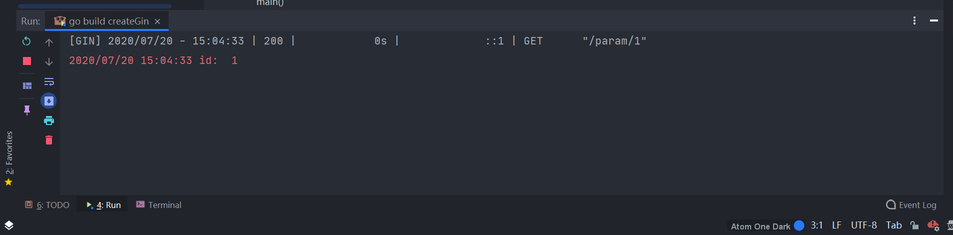
-
通过 Body 传参
Body 传参是指将参数放在请求体内部的传参形式,多用于 POST 请求。
在 Gin 中可以通过
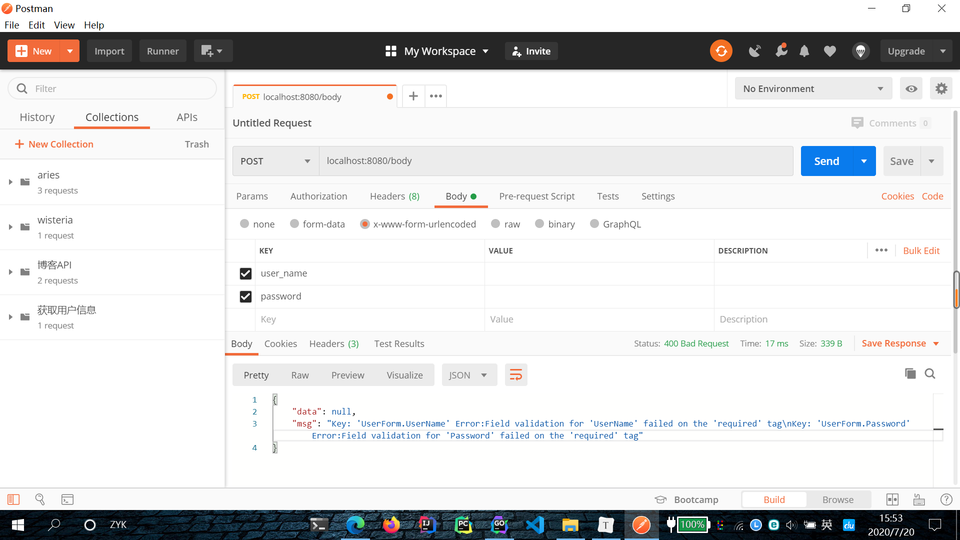
context.PostForm("参数名称")来获取参数的值。// 通过 Body 传参 router.POST("/body", func(context *gin.Context) { username := context.PostForm("username") password := context.PostForm("password") log.Println("username: ", username) log.Println("password: ", password) })运行项目,打开 Postman 进行 API 测试,观察 Goland 控制台信息。
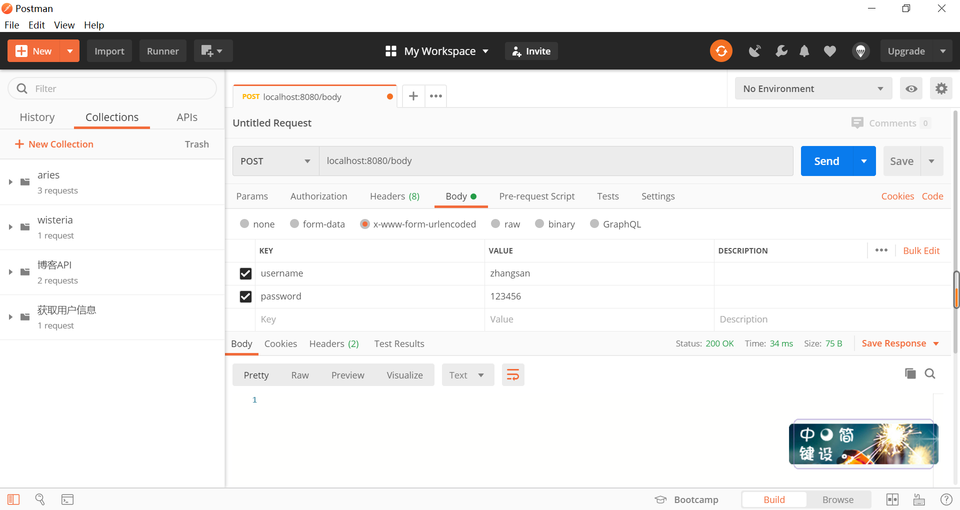
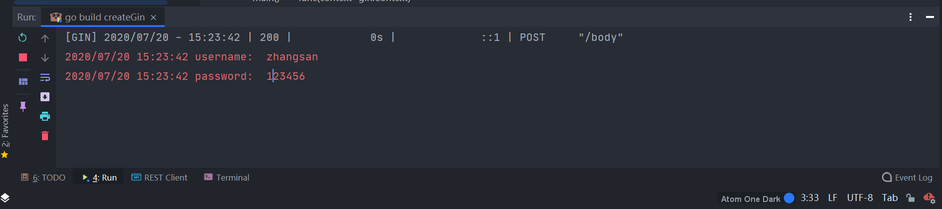
参数校验
如果手动对参数进行校验,一旦参数过多,将会非常麻烦。Gin 内置了参数校验库 github.com/go-playground/validator/v10,我们直接调用它即可。
首先定义一个表单结构体 UserForm;
form:"user_name" 表示参数类型是 form,参数名称为 user_name;
binding:"required,min=3,max=20" 是表单校验的内容,required 表示必填字段,min=3 表示最短长度为 3,max=20 表示最大长度为 20。更多字段校验形式可以参考 https://github.com/go-playground/validator 。
// 用户表单
type UserForm struct {
UserName string `form:"user_name" binding:"required,min=3,max=20"` // 用户名
Password string `form:"password" binding:"required,min=6,max=20"` // 密码
}
通过 ShouldBind 函数将请求数据绑定到表单上:
// 表单校验
router.POST("/body", func(context *gin.Context) {
form := UserForm{}
// 绑定参数到 form
err := context.ShouldBind(&form)
// 表单错误处理
if err != nil {
// 返回 JSON
context.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"msg": err.Error(),
"data": nil,
})
return
}
// 返回 JSON
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"msg": "数据校验成功",
"data": nil,
})
})
运行项目,用 Postman 进行测试。